Structure and mechanism of cancer-associated N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-V.
Nagae, M., Kizuka, Y., Mihara, E., Kitago, Y., Hanashima, S., Ito, Y., Takagi, J., Taniguchi, N., Yamaguchi, Y.(2018) Nat Commun 9: 3380-3380
- PubMed: 30140003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05931-w
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5ZIB, 5ZIC - PubMed Abstract:
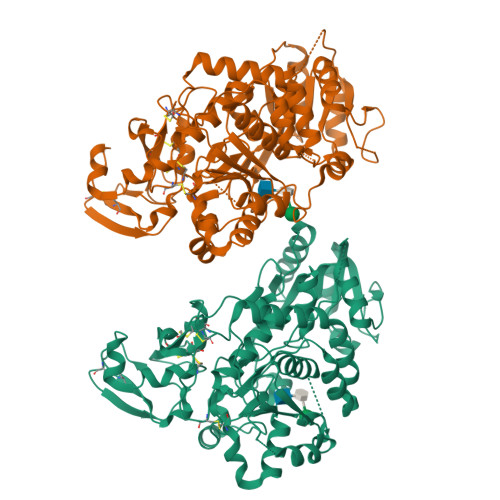
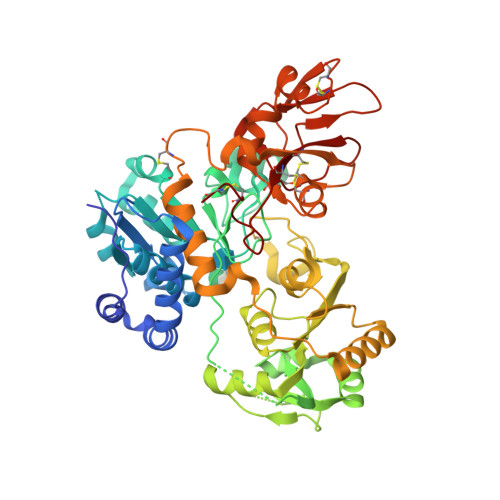
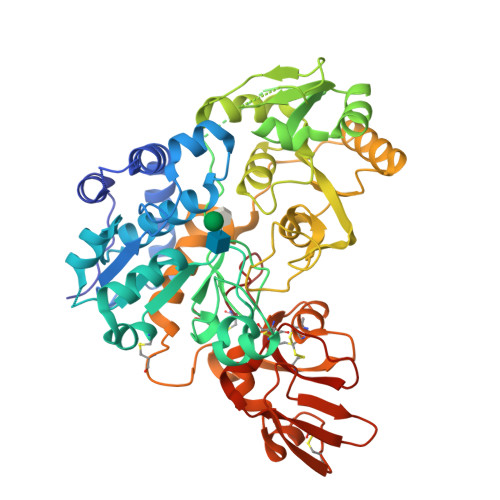
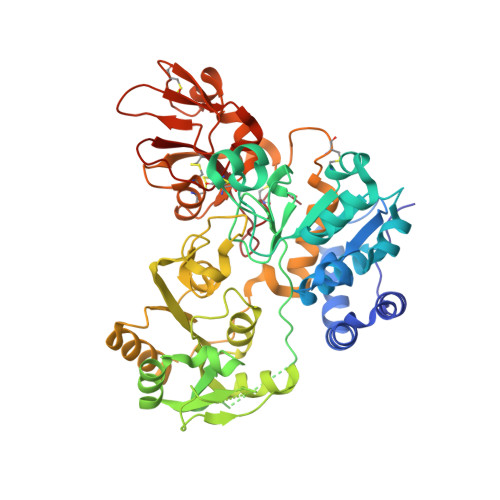
N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase-V (GnT-V) alters the structure of specific N-glycans by modifying α1-6-linked mannose with a β1-6-linked N-acetylglucosamine branch. β1-6 branch formation on cell surface receptors accelerates cancer metastasis, making GnT-V a promising target for drug development. However, the molecular basis of GnT-V's catalytic mechanism and substrate specificity are not fully understood. Here, we report crystal structures of human GnT-V luminal domain with a substrate analog. GnT-V luminal domain is composed of a GT-B fold and two accessary domains. Interestingly, two aromatic rings sandwich the α1-6 branch of the acceptor N-glycan and restrain the global conformation, partly explaining the fine branch specificity of GnT-V. In addition, interaction of the substrate N-glycoprotein with GnT-V likely contributes to protein-selective and site-specific glycan modification. In summary, the acceptor-GnT-V complex structure suggests a catalytic mechanism, explains the previously observed inhibition of GnT-V by branching enzyme GnT-III, and provides a basis for the rational design of drugs targeting N-glycan branching.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Glycobiology Team, Glycobiology Research Group, Global Research Cluster, RIKEN, 2-1 Hirosawa, Wako, Saitama, 351-0198, Japan. mnagae@mol.f.u-tokyo.ac.jp.