New Crystallographic Snapshots of Large Domain Movements in Bacterial 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl Coenzyme A Reductase.
Ragwan, E.R., Arai, E., Kung, Y.(2018) Biochemistry 57: 5715-5725
- PubMed: 30199631
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00869
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6DIO, 6EEU, 6EEV - PubMed Abstract:
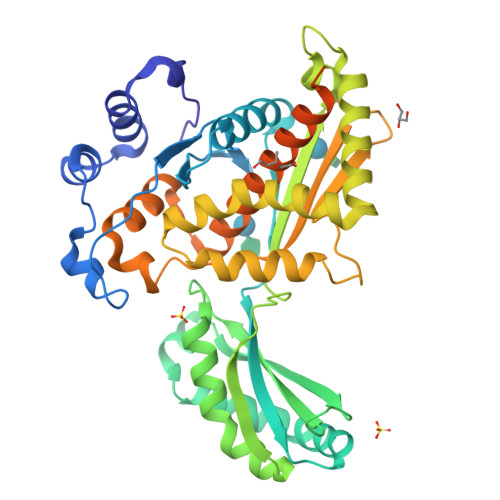
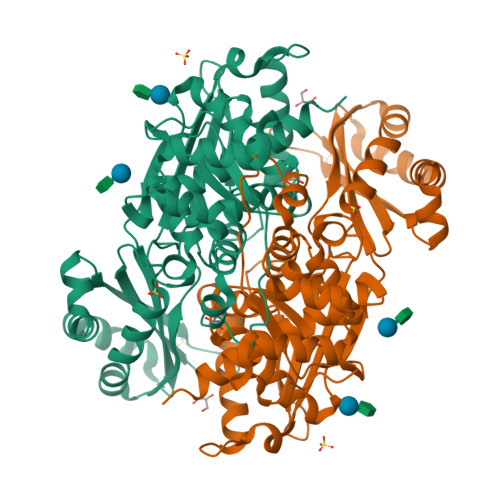
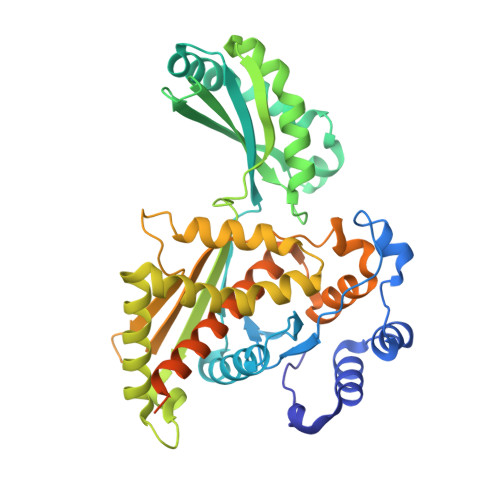
The enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase (HMGR) catalyzes the first committed step of the mevalonate pathway, which is used across biology in the biosynthesis of countless metabolites. HMGR consumes 2 equiv of the cofactor NAD(P)H to perform the four-electron reduction of HMG-CoA to mevalonate toward the production of steroids and isoprenoids, the largest class of natural products. Recent structural data have shown that HMGR contains a highly mobile C-terminal domain (CTD) that is believed to adopt many different conformations to permit binding and dissociation of the substrate, cofactors, and products at specific points during the reaction cycle. Here, we have characterized the HMGR from Delftia acidovorans as an NADH-specific enzyme and determined crystal structures of the enzyme in unbound, mevalonate-bound, and NADH- and citrate-bound states. Together, these structures depict ligand binding in both the active site and the cofactor-binding site while illustrating how a conserved helical motif confers NAD(P)H cofactor specificity. Unexpectedly, the NADH-bound structure also reveals a new conformation of the CTD, in which the domain has "flipped" upside-down, while directly binding the cofactor. By capturing these structural snapshots, this work not only expands the known range of HMGR domain movement but also provides valuable insight into the catalytic mechanism of this biologically important enzyme.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry , Bryn Mawr College , 101 North Merion Avenue , Bryn Mawr , Pennsylvania 19010 , United States.