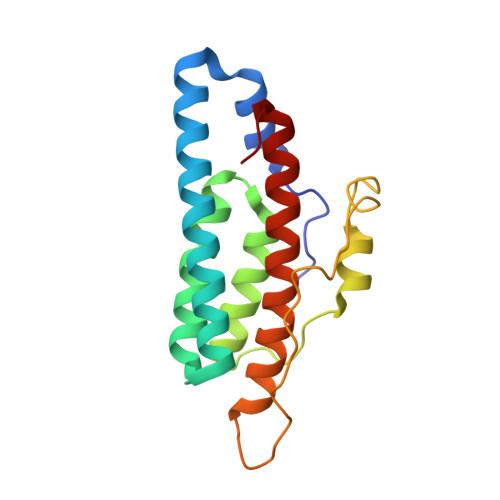
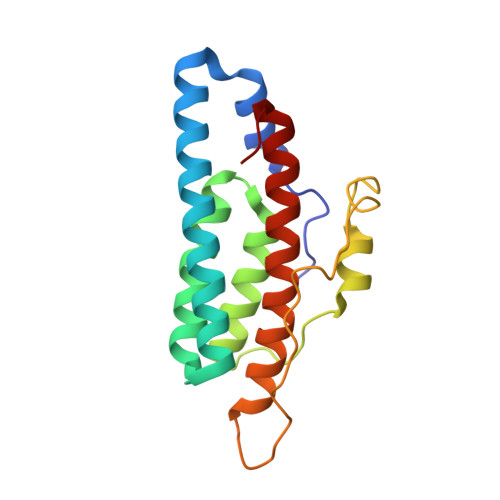
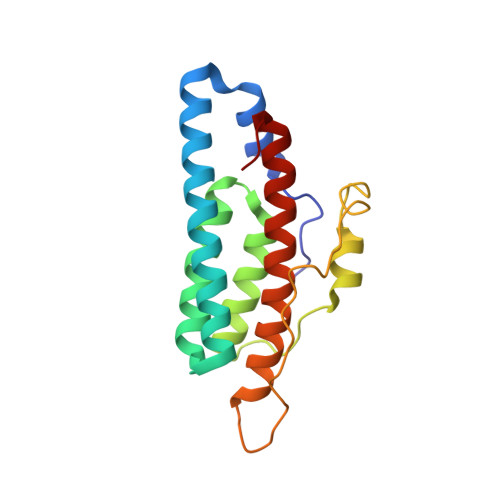
Role of the highly conserved G68 residue in the yeast phosphorelay protein Ypd1: implications for interactions between histidine phosphotransfer (HPt) and response regulator proteins.
Kennedy, E.N., Hebdon, S.D., Menon, S.K., Foster, C.A., Copeland, D.M., Xu, Q., Janiak-Spens, F., West, A.H.(2019) BMC Biochem 20: 1-1
- PubMed: 30665347
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12858-019-0104-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6M7W - PubMed Abstract:
Many bacteria and certain eukaryotes utilize multi-step His-to-Asp phosphorelays for adaptive responses to their extracellular environments. Histidine phosphotransfer (HPt) proteins function as key components of these pathways. HPt proteins are genetically diverse, but share a common tertiary fold with conserved residues near the active site. A surface-exposed glycine at the H + 4 position relative to the phosphorylatable histidine is found in a significant number of annotated HPt protein sequences. Previous reports demonstrated that substitutions at this position result in diminished phosphotransfer activity between HPt proteins and their cognate signaling partners. We report the analysis of partner binding interactions and phosphotransfer activity of the prototypical HPt protein Ypd1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae using a set of H + 4 (G68) substituted proteins. Substitutions at this position with large, hydrophobic, or charged amino acids nearly abolished phospho-acceptance from the receiver domain of its upstream signaling partner, Sln1 (Sln1-R1). An in vitro binding assay indicated that G68 substitutions caused only modest decreases in affinity between Ypd1 and Sln1-R1, and these differences did not appear to be large enough to account for the observed decrease in phosphotransfer activity. The crystal structure of one of these H + 4 mutants, Ypd1-G68Q, which exhibited a diminished ability to participate in phosphotransfer, shows a similar overall structure to that of wild-type. Molecular modelling suggests that the highly conserved active site residues within the receiver domain of Sln1 must undergo rearrangement to accommodate larger H + 4 substitutions in Ypd1. Phosphotransfer reactions require precise arrangement of active site elements to align the donor-acceptor atoms and stabilize the transition state during the reaction. Any changes likely result in an inability to form a viable transition state during phosphotransfer. Our data suggest that the high degree of evolutionary conservation of residues with small side chains at the H + 4 position in HPt proteins is required for optimal activity and that the presence of larger residues at the H + 4 position would cause alterations in the positioning of active site residues in the partner response regulator.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, 73019, USA.