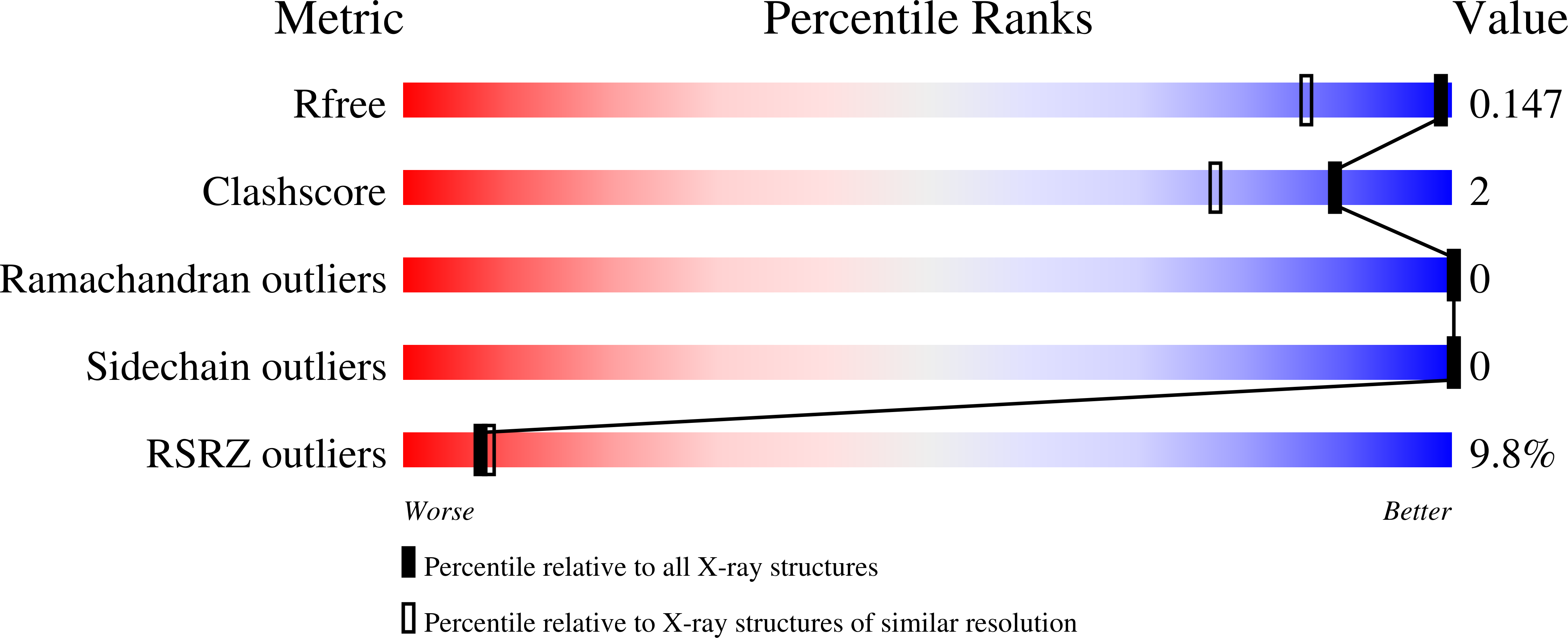
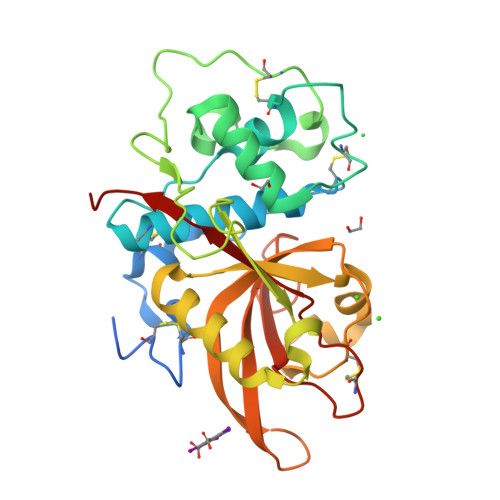
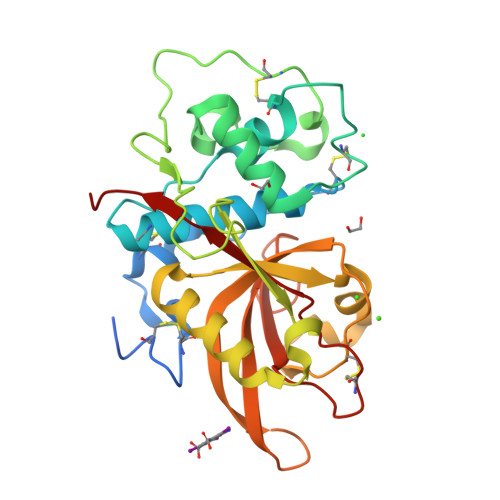
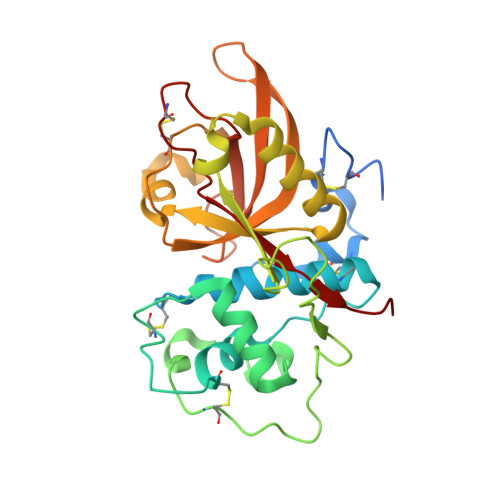
Structure of the Plasmodium falciparum PfSERA5 pseudo-zymogen.
Smith, N.A., Clarke, O.B., Lee, M., Hodder, A.N., Smith, B.J.(2020) Protein Sci 29: 2245-2258
- PubMed: 32955133
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3956
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6X42, 6X44 - PubMed Abstract:
PfSERA5, a significantly abundant protein present within the parasitophorous vacuole (PV) and essential for normal growth during the blood-stage life cycle of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum, displays structural similarity to many other cysteine proteases. However, PfSERA5 does not exhibit any detectable protease activity and therefore the role of the PfSERA5 papain-like domain (PfSERA5E), thought to remain bound to its cognate prodomain, remains unknown. In this study, we present a revised structure of the central PfSERA5E domain at a resolution of 1.2 Å, and the first structure of the "zymogen" of this papain-like domain including its cognate prodomain (PfSERA5PE) to 2.2 Å resolution. PfSERA5PE is somewhat structurally similar to that of other known proenzymes, retaining the conserved overall folding and orientation of the prodomain through, and occluding, the archetypal papain-like catalytic triad "active-site" cleft, in the same reverse direction as conventional prodomains. Our findings are congruent with previously identified structures of PfSERA5E and of similar "zymogens" and provide a foundation for further investigation into the function of PfSERA5.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry and Physics, La Trobe Institute for Molecular Science, La Trobe University, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.