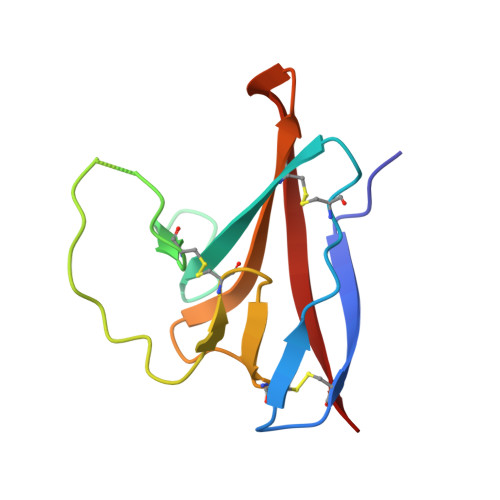
Glycosylated, Lipid-Binding, CDR-Like Domains of SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 Indicate Unique Sites of Immune Regulation.
Wu, F., Chen, X., Ma, Y., Wu, Y., Li, R., Huang, Y., Zhang, R., Zhou, Y., Zhan, J., Liu, S., Xu, W.(2023) Microbiol Spectr 11: e0123423-e0123423
- PubMed: 37318366
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/spectrum.01234-23
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7XMN - PubMed Abstract:
The outbreak of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 has posed a significant threat to human health and the global economy since the end of 2019. Unfortunately, due to the virus's rapid evolution, preventingand controlling the epidemic remains challenging. The ORF8 protein is a unique accessory protein in SARS-CoV-2 that plays a crucial role in immune regulation, but its molecular details are still largely unknown. In this study, we successfully expressed SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 in mammalian cells and determined its structure using X-ray crystallography at a resolution of 2.3 Å. Our findings reveal several novel features of ORF8. We found that four pairs of disulfide bonds and glycosylation at residue N78 are essential for stabilizing ORF8's protein structure. Additionally, we identified a lipid-binding pocket and three functional loops that tend to form CDR-like domains that may interact with immune-related proteins to regulate the host immune system. On cellular experiments also demonstrated that glycosylation at N78 regulats of ORF8's ability to bind to monocytes cells. These novel features of ORF8 provide structural insights to into its immune-related function and may serve as new targets for developing ORF8-mediated immune regulation inhibitors. IMPORTANCE COVID-19, caused by the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 virus, has triggered a global outbreak. The virus's continuous mutation increases its infectivity and may be directly related to the immune escape response of viral proteins. In this study, we used X-ray crystallography to determine the structure of SARS-CoV-2 ORF8 protein, a unique accessory protein expressed in mammalian cells, at a resolution of 2.3 Å. Our novel structure reveals important structure details that shed light on ORF8's involvement in immune regulation, including conservation disulfide bonds, a glycosylation site at N78, a lipid-binding pocket, and three functional loops that tend to form CDR-like domains that may interact with immune-related proteins to modulate the host immune system. We also conducted preliminary validation experiments on immune cells. These new insights into ORF8's structure and function provide potential targets for developing inhibitors to block the ORF8-mediated immune regulation between viral protein and host, ultimately contributing to the development of novel therapeutics for COVID-19.
Organizational Affiliation:
Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of New Drug Screening, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China.