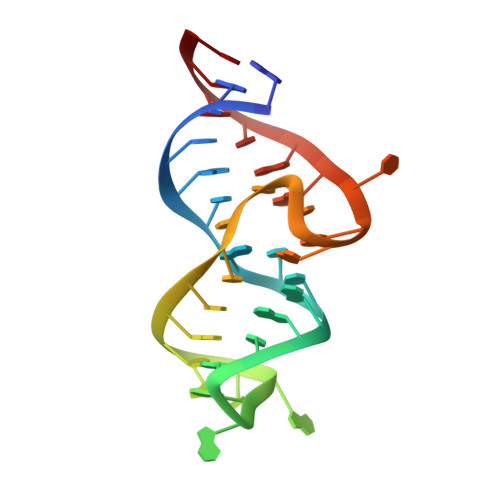
Discovery of small molecules that target a tertiary-structured RNA.
Menichelli, E., Lam, B.J., Wang, Y., Wang, V.S., Shaffer, J., Tjhung, K.F., Bursulaya, B., Nguyen, T.N., Vo, T., Alper, P.B., McAllister, C.S., Jones, D.H., Spraggon, G., Michellys, P.Y., Joslin, J., Joyce, G.F., Rogers, J.(2022) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 119: e2213117119-e2213117119
- PubMed: 36413497
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2213117119
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8D28, 8D29, 8D2A, 8D2B, 8D5L, 8D5O, 8DK7 - PubMed Abstract:
There is growing interest in therapeutic intervention that targets disease-relevant RNAs using small molecules. While there have been some successes in RNA-targeted small-molecule discovery, a deeper understanding of structure-activity relationships in pursuing these targets has remained elusive. One of the best-studied tertiary-structured RNAs is the theophylline aptamer, which binds theophylline with high affinity and selectivity. Although not a drug target, this aptamer has had many applications, especially pertaining to genetic control circuits. Heretofore, no compound has been shown to bind the theophylline aptamer with greater affinity than theophylline itself. However, by carrying out a high-throughput screen of low-molecular-weight compounds, several unique hits were identified that are chemically distinct from theophylline and bind with up to 340-fold greater affinity. Multiple atomic-resolution X-ray crystal structures were determined to investigate the binding mode of theophylline and four of the best hits. These structures reveal both the rigidity of the theophylline aptamer binding pocket and the opportunity for other ligands to bind more tightly in this pocket by forming additional hydrogen-bonding interactions. These results give encouragement that the same approaches to drug discovery that have been applied so successfully to proteins can also be applied to RNAs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Novartis Institutes for BioMedical Research, San Diego, CA 92121.