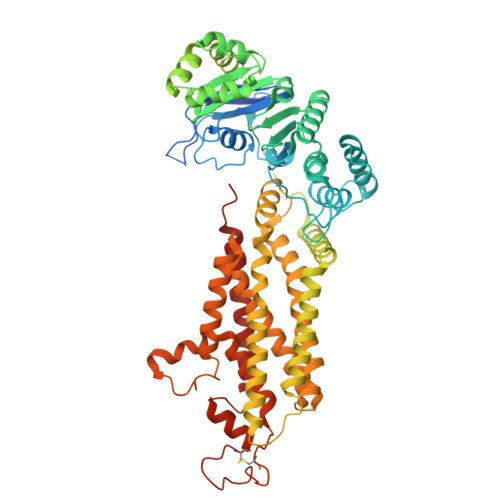
Modulation of ABCG2 Transporter Activity by Ko143 Derivatives.
Yu, Q., Dehghani-Ghahnaviyeh, S., Rasouli, A., Sadurni, A., Kowal, J., Bang-Soerensen, R., Wen, P.C., Tinzl-Zechner, M., Irobalieva, R.N., Ni, D., Stahlberg, H., Altmann, K.H., Tajkhorshid, E., Locher, K.P.(2024) ACS Chem Biol
- PubMed: 39445888
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.4c00353
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8PXO, 8PY4, 8Q7B, 8QCM - PubMed Abstract:
ABCG2 is a multidrug transporter that protects tissues from xenobiotics, affects drug pharmacokinetics, and contributes to multidrug resistance of cancer cells. Here, we present tetracyclic fumitremorgin C analog Ko143 derivatives, evaluate their in vitro modulation of purified ABCG2, and report four high-resolution cryo-EM structures and computational analyses to elucidate their interactions with ABCG2. We found that Ko143 derivatives that are based on a ring-opened scaffold no longer inhibit ABCG2-mediated transport activity. In contrast, closed-ring, tetracyclic analogs were highly potent inhibitors. Strikingly, the least potent of these compounds, MZ82, bound deeper into the central ABCG2 cavity than the other inhibitors and it led to partial closure of the transmembrane domains and increased flexibility of the nucleotide-binding domains. Minor structural modifications can thus convert a potent inhibitor into a compound that induces conformational changes in ABCG2 similar to those observed during binding of a substrate. Molecular dynamics simulations and free energy binding calculations further supported the correlation between reduced potency and distinct binding pose of the compounds. We introduce the highly potent inhibitor AZ99 that may exhibit improved in vivo stability.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institute of Molecular Biology and Biophysics, Department of Biology, ETH Zurich, Zurich 8093, Switzerland.