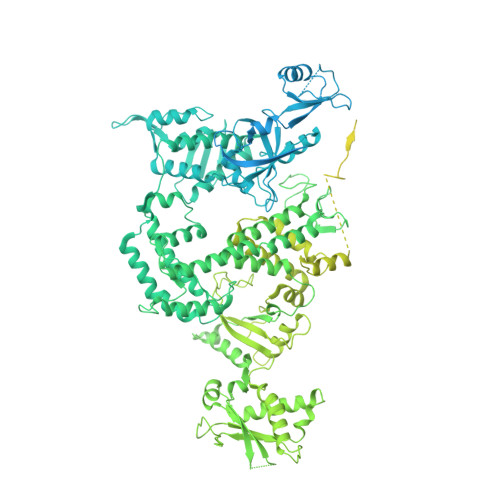
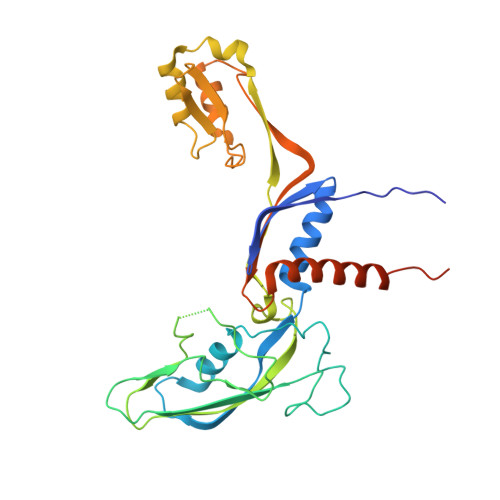
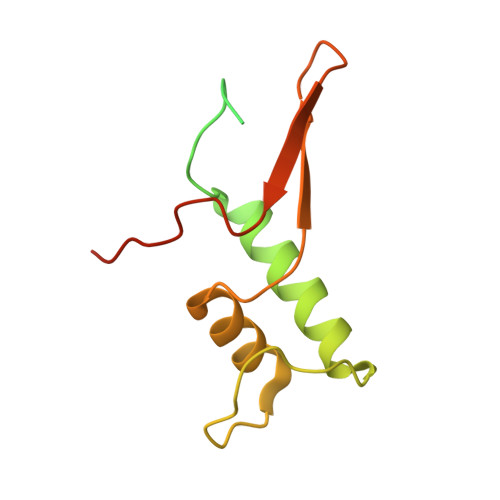
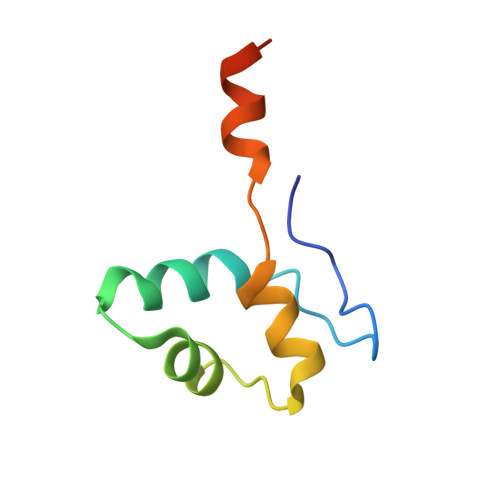
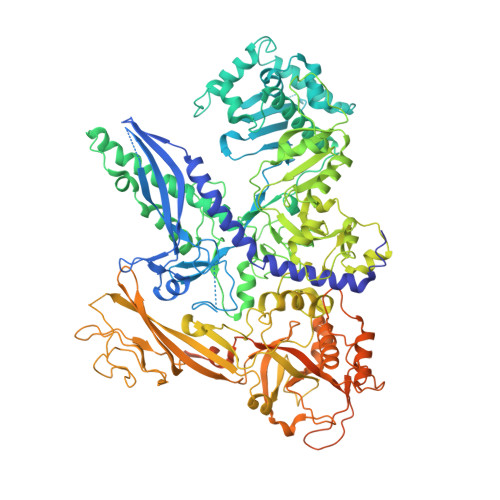
Structure and mechanism of the plant RNA polymerase V.
Xie, G., Du, X., Hu, H., Li, S., Cao, X., Jacobsen, S.E., Du, J.(2023) Science 379: 1209-1213
- PubMed: 36893216
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adf8231
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8HIL, 8HIM - PubMed Abstract:
In addition to the conserved RNA polymerases I to III (Pols I to III) in eukaryotes, two atypical polymerases, Pols IV and V, specifically produce noncoding RNA in the RNA-directed DNA methylation pathway in plants. Here, we report on the structures of cauliflower Pol V in the free and elongation conformations. A conserved tyrosine residue of NRPE2 stacks with a double-stranded DNA branch of the transcription bubble to potentially attenuate elongation by inducing transcription stalling. The nontemplate DNA strand is captured by NRPE2 to enhance backtracking, thereby increasing 3'-5' cleavage, which likely underpins Pol V's high fidelity. The structures also illuminate the mechanism of Pol V transcription stalling and enhanced backtracking, which may be important for Pol V's retention on chromatin to serve its function in tethering downstream factors for RNA-directed DNA methylation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Key Laboratory of Molecular Design for Plant Cell Factory of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Institute of Plant and Food Science, Department of Biology, School of Life Sciences, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen 518055, China.