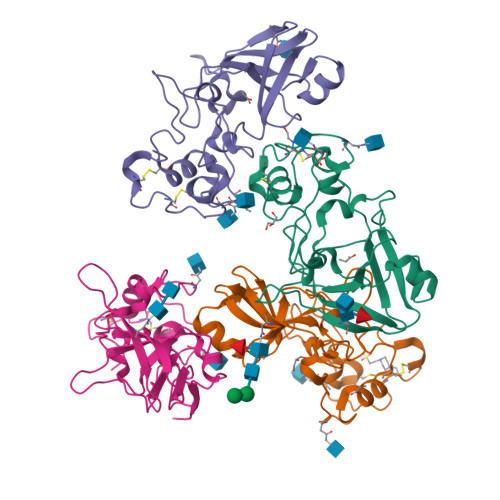
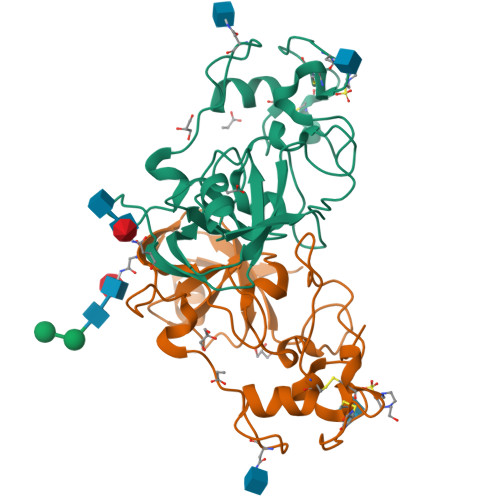
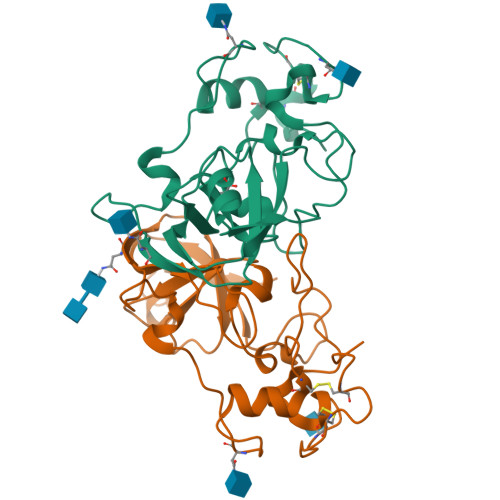
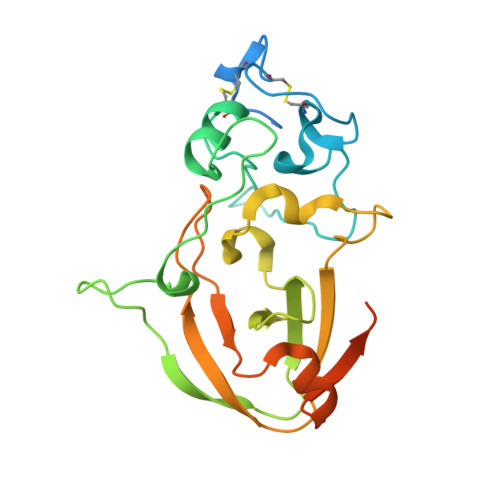
Novel Calcium-Binding Motif Stabilizes and Increases the Activity of Aspergillus fumigatus Ecto-NADase.
Ferrario, E., Kallio, J.P., Stromland, O., Ziegler, M.(2023) Biochemistry 62: 3293-3302
- PubMed: 37934975
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.3c00360
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8PMR, 8PMS - PubMed Abstract:
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is an essential molecule in all kingdoms of life, mediating energy metabolism and cellular signaling. Recently, a new class of highly active fungal surface NADases was discovered. The enzyme from the opportunistic human pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus was thoroughly characterized. It harbors a catalytic domain that resembles that of the tuberculosis necrotizing toxin from Mycobacterium tuberculosis , which efficiently cleaves NAD + to nicotinamide and ADP-ribose, thereby depleting the dinucleotide pool. Of note, the A. fumigatus NADase has an additional Ca 2+ -binding motif at the C-terminus of the protein. Despite the presence of NADases in several fungal divisions, the Ca 2+ -binding motif is uniquely found in the Eurotiales order, which contains species that have immense health and economic impacts on humans. To identify the potential roles of the metal ion-binding site in catalysis or protein stability, we generated and characterized A. fumigatus NADase variants lacking the ability to bind calcium. X-ray crystallographic analyses revealed that the mutation causes a drastic and dynamic structural rearrangement of the homodimer, resulting in decreased thermal stability. Even though the calcium-binding site is at a long distance from the catalytic center, the structural reorganization upon the loss of calcium binding allosterically alters the active site, thereby negatively affecting NAD-glycohydrolase activity. Together, these findings reveal that this unique calcium-binding site affects the protein fold, stabilizing the dimeric structure, but also mediates long-range effects resulting in an increased catalytic rate.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biomedicine, University of Bergen, Jonas Lies vei 91, Bergen 5009, Norway.